Throughout this post we will try to cover what phishing is, how it works and how you can protect yourself against these attacks.
Phishing is one of the most common methods used by cybercriminals to scam and fraudulently obtain sensitive information. This can be a password or detailed information about the victim’s credit card or other banking information.
The scammer, known as a phisher, uses social engineering techniques and poses as a trustworthy person or company in an apparent official electronic communication. Usually through an email or instant messaging system, social networks, SMS/MMS, following malware or even using phone calls as well. There are different phishing attacks, such asl email spoofing y el spear phishing.
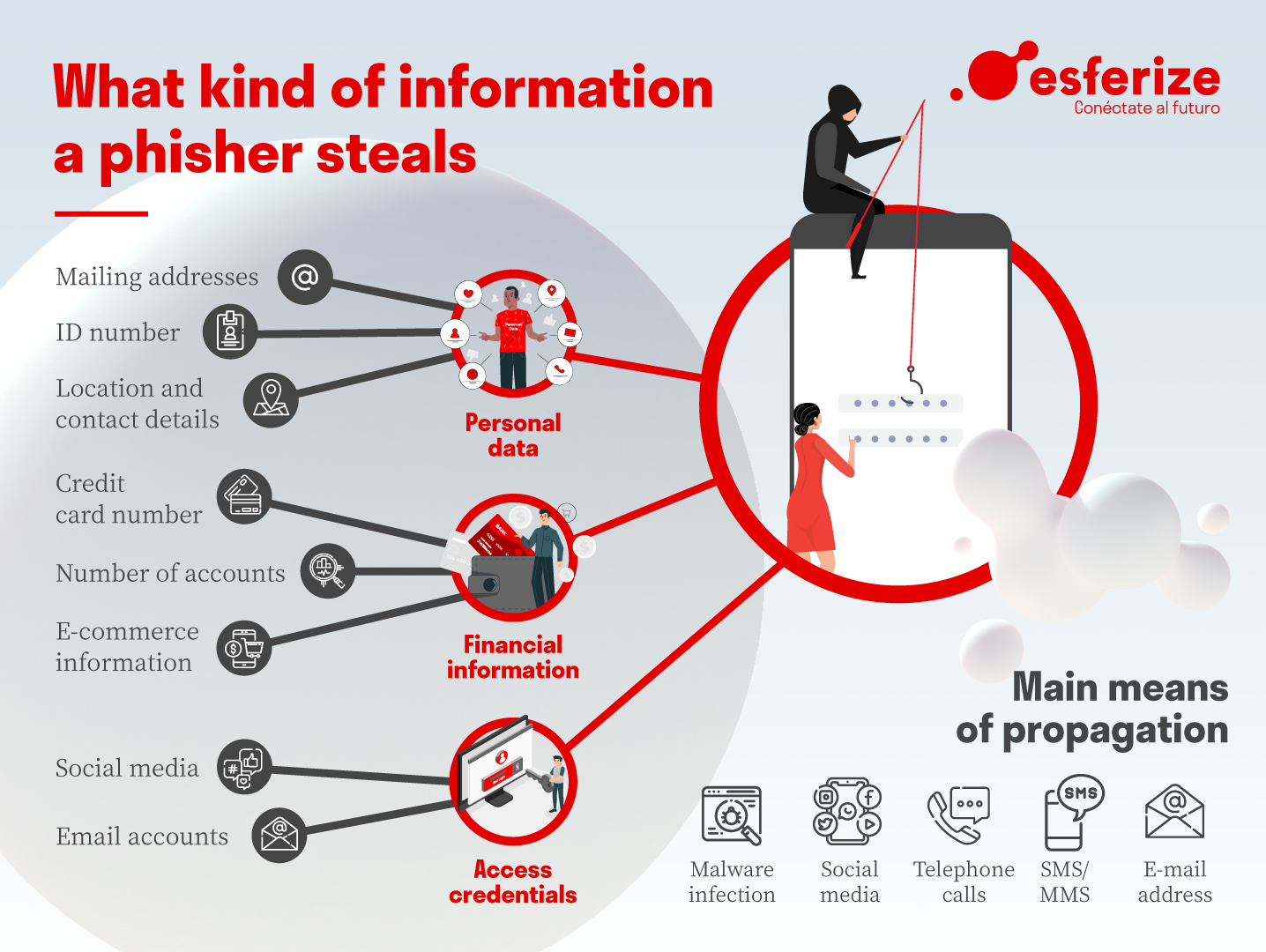
What kind of information does it steal and how is it distributed?
What does the circuit of one of these attacks look like?
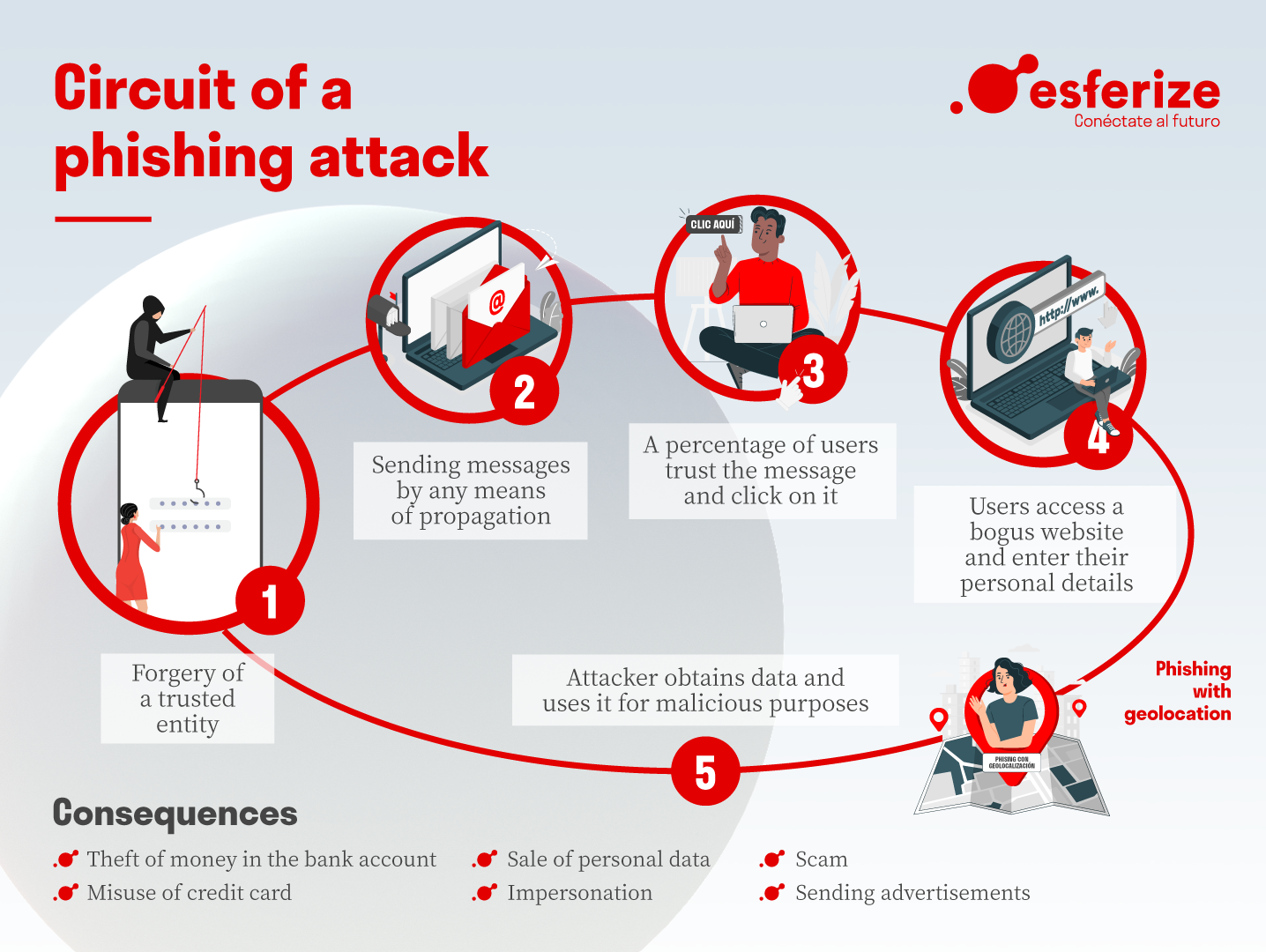
Geolocation phishing is a technique used to allow or deny access to the fake website to users from a certain country, by means of the IP address or a proxy server. Any unauthorised access from another part of the world will not be able to access the phishing page. The aim is to make these attacks more effective by being more likely to reach the users of the original site.
How much could a cyberattacker get away with?
Now that we know what kind of information a phisher steals, by what means and what steps a phishing attack always follows, we ask ourselves… How much could he or she make?
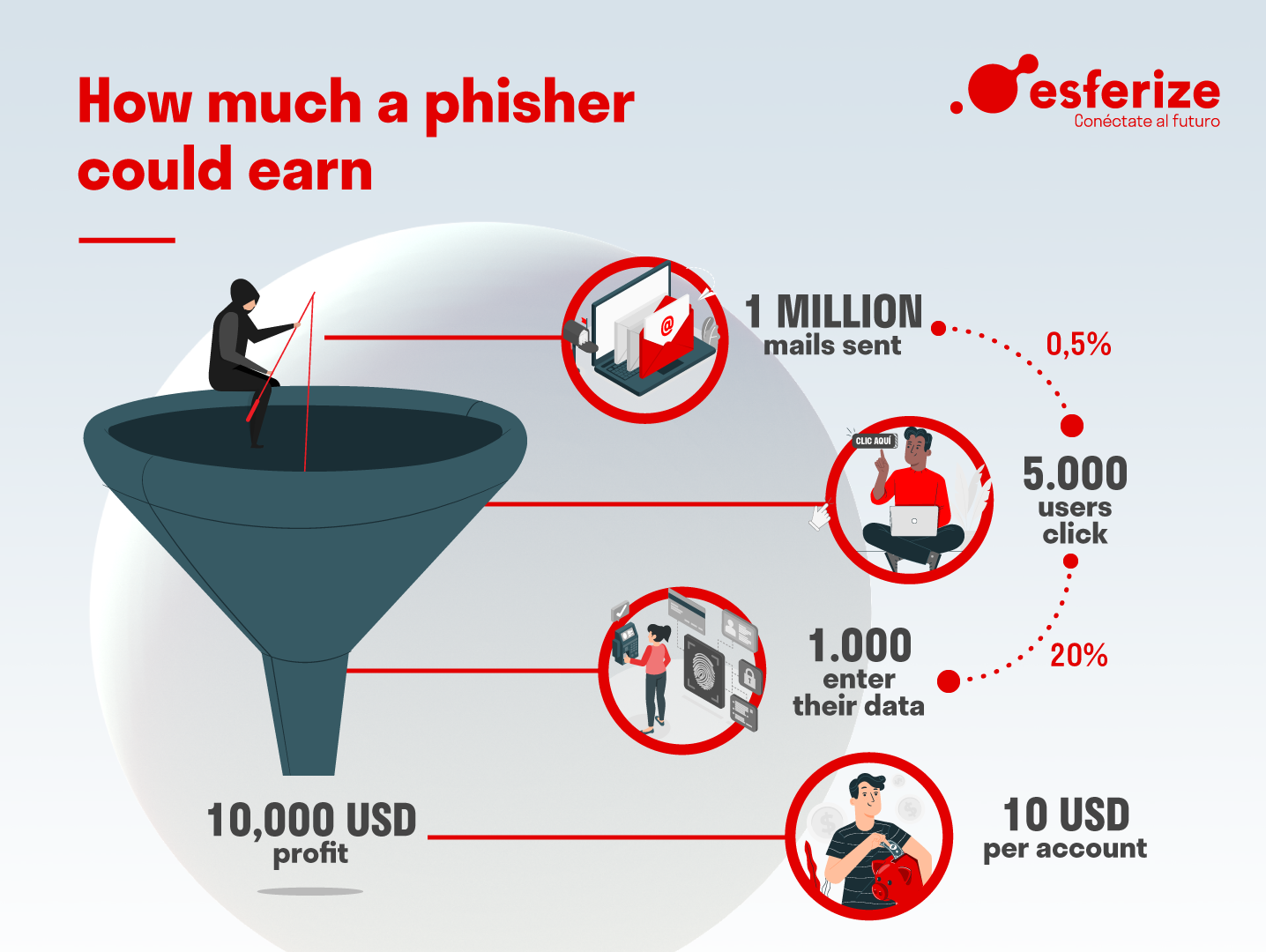
Cyber-attacks are like a funnel. Imagine that:
- The phisher sends 1,000,000 emails.
- Only 0.5% of the users who have received the communication, i.e. 5,000, click on it.
- 20% of them, i.e. 1,000 people, also enter their data.
- In total, in this type of simple attack, 10 USD per account was stolen.
- Result: 10,000 USD profit.
To prevent these cyber-attacks, remember:
1. Learn how to identify suspicious emails.
- They use names and adopt the image of real companies.
- They have the name of the company or that of an employee as the sender.
- They include websites that are visually the same as real companies.
- They use gifts or the loss of the existing account as a hook.
2. Verify the source of information in your incoming emails.
- Your bank will never ask you to send them your passwords or personal details by post.
- Do not answer such questions.
- If you have any doubts, call your bank directly for clarification.
3. Never access your bank’s website by clicking on links in emails.
- Do not click on the links, as they may covertly direct you to a fraudulent website.
- Type the web address directly into your browser.
4. Strengthen the security of your computer by using an antivirus.
- In addition, you should always keep your operating system and web browsers up to date.
5. Enter your confidential data only on secure websites.
- Pay attention that they start with https:// and that they appear with a small closed padlock icon.
6. Periodically review your bank accounts to be aware of any irregularities in your transactions.
7. Phishing is not just about online banking.
- In reality, they do not only impersonate banks.
- They can use any other popular website of the moment to steal personal data: eBay, Facebook, PayPal, etc.
8. Phishing knows languages.
- Phishing knows no borders and attacks can reach you in any language.
- They are usually poorly written or translated, so this can be another indicator that something is wrong.
9. When in doubt, be cautious and don’t take risks.
10. Be regularly updated on the latest malware attacks.
- Don’t forget to follow us to stay up to date on cybersecurity.
Source: InfoSpyware.com





